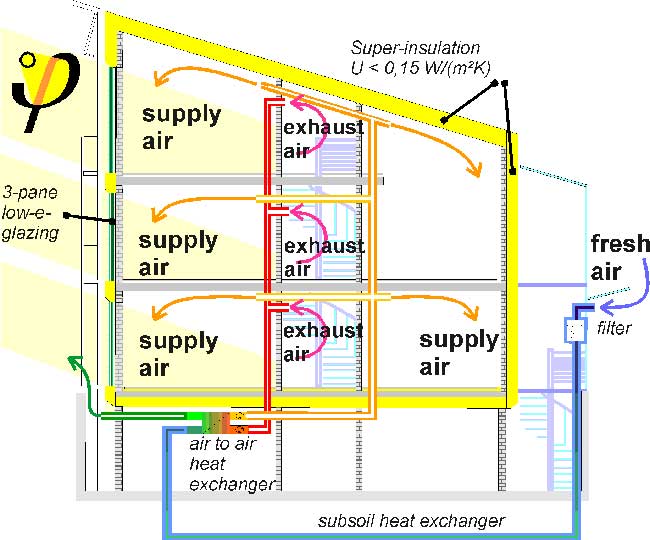
The Passive House standard is the world’s highest and fastest growing energy efficiency standard that achieves a reduction in energy consumption up to 90%. There are now more than 30,000 passive buildings around the world, many of which have been built since 2000. Passive house is a super-isolated, almost hermetic building. The heating is done by the passive accumulation of energy from the sun, the electrical equipment and also by the energy of the people living in it. The remaining heat is provided by an extremely small heat source. Passive building thermostats are limited to a minimum to reduce heat loss.
Avoiding heat overheating through the orientation of the house and high-quality triple-glazed windows, help to reduce the need for additional cooling, which is often unnecessary. The passive house has a recovery system with a recuperator for energy utilization and recovery, balanced and constant supply of fresh air. The result is an impressive overall system that not only saves up to 90% of heating costs but also provides superb air quality.
Characteristics that are mandatory for the Passive House standard:
- Annual energy demand for heating and ventilation ≤ 15 kWh / sq.m / per year
- Annual consumption for all needs of the building ≤ 120 kWh / sq. m / per year
- Building air impermeability ≤ 0.6 ACH @ 50 pascal load measured in a Blower-door test.
Additional Climate Requirements:
- Windows with U – values - ≤ 0.8 W / m2 / K
- Ventilation system with energy utilization and efficiency ≤ 75% and with low electrical consumption of 0.45 Wh / cubic meter
- Construction without thermal bridges ≤ 0.01 W / mK
- Picture rights by PHI